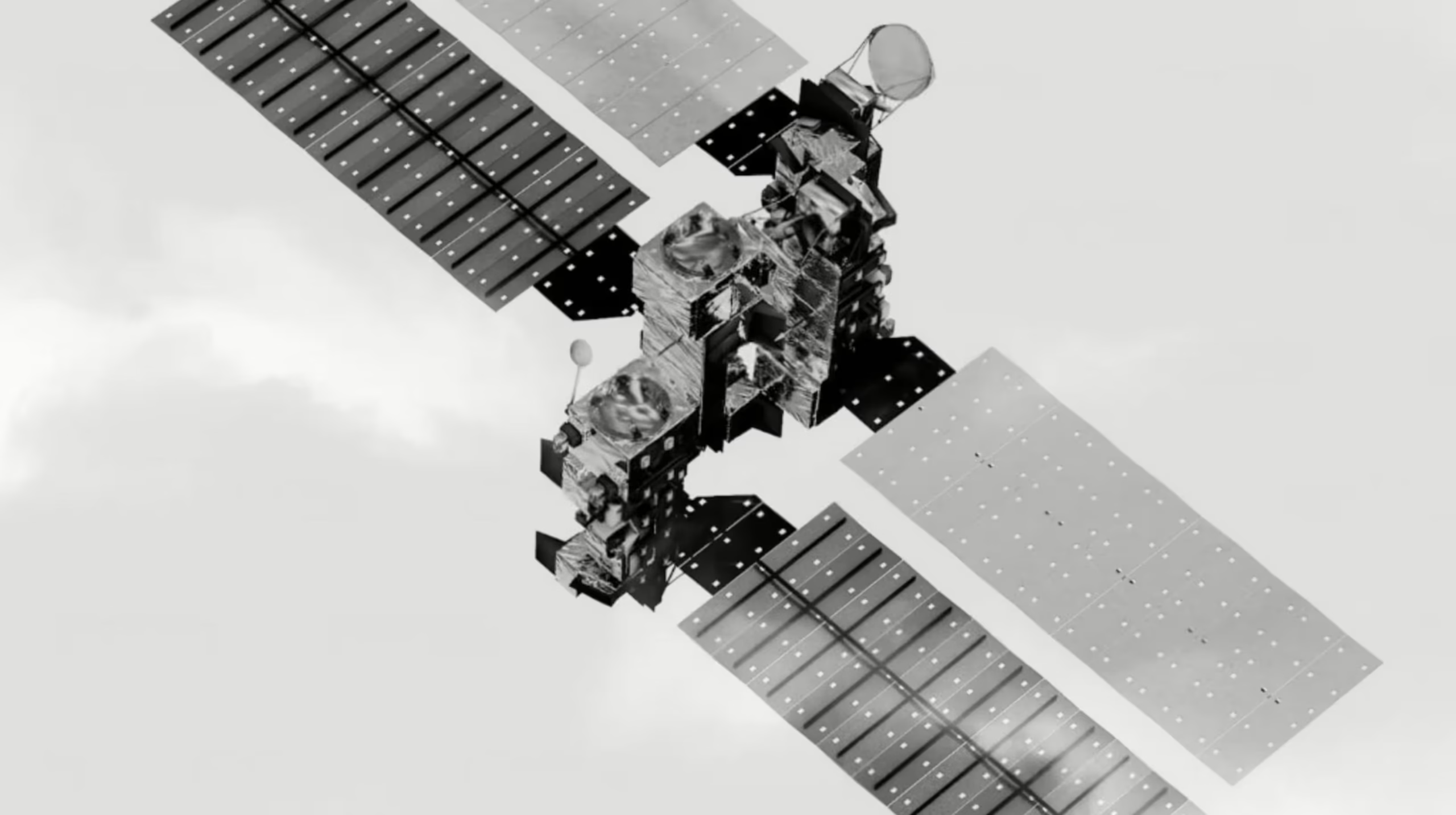
Artificial intelligence has reached a historic milestone. For the first time, large language models (LLMs) have been trained beyond Earth’s atmosphere. Starcloud, an emerging space-compute company, has successfully trained LLMs in orbit using NVIDIA’s powerful H100 GPUs—marking the dawn of off-world artificial intelligence.
This breakthrough signals more than a technological first. It represents a fundamental shift in how and where advanced computing can exist, pushing cloud infrastructure, AI scalability, and data processing into the final frontier: space.
AI Reaches Orbit: A Historic First
Until now, all major AI training has occurred on Earth, inside massive data centers constrained by land, energy availability, cooling demands, and geopolitical boundaries. Starcloud’s achievement breaks this limitation by demonstrating that high-performance AI training is possible in orbit.
By moving LLM training into space, Starcloud has proven that AI infrastructure no longer needs to be Earth-bound. This milestone opens the door to a future where computing power is distributed across the planet—and beyond it.
Why Train Large Language Models in Space?
Training modern LLMs is extremely resource-intensive. On Earth, it requires:
- Gigawatts of electricity
- Advanced cooling systems
- Massive physical infrastructure
- High environmental cost
Space offers unique advantages that directly address these challenges:
- Natural cooling: The vacuum of space enables efficient heat dissipation without traditional cooling systems.
- Abundant solar energy: Orbiting platforms can harness near-continuous solar power.
- No land constraints: Space eliminates competition for physical real estate.
- Infrastructure scalability: Orbital platforms can scale without urban or regulatory limits.
Starcloud’s experiment validates that space is not just viable—but potentially optimal—for AI training.
NVIDIA H100: Powering AI Beyond Earth
At the heart of this breakthrough is NVIDIA’s H100 GPU, one of the most advanced AI accelerators ever built. Designed for extreme-scale AI workloads, the H100 delivers:
- Massive parallel processing
- High memory bandwidth
- Optimized tensor cores for LLM training
- Advanced fault tolerance
Starcloud’s successful deployment demonstrates that the H100 can operate reliably even in microgravity and radiation-prone environments, proving its readiness for space-based computing.
This milestone also marks a symbolic moment: NVIDIA’s AI hardware has officially left Earth.
Training LLMs in Microgravity: What’s Different?
Training AI models in space introduces entirely new conditions:
- Microgravity: Eliminates mechanical stress common in Earth-based systems
- Radiation exposure: Requires hardened systems and robust error correction
- Latency challenges: Data transfer between Earth and orbit must be optimized
Starcloud overcame these challenges through a combination of hardened compute modules, autonomous fault correction, and edge-training strategies—where models are trained and refined in orbit before being transmitted back to Earth.
This sets the stage for self-operating AI systems in space.
Space-Based Computing Infrastructure: Redefining the Cloud
Starcloud’s success hints at a future where the “cloud” is no longer grounded. Instead, computing infrastructure could exist as:
- Orbital AI clusters
- Autonomous space data centers
- Satellite-based training platforms
- AI-powered orbital edge nodes
Such infrastructure could support Earth-based applications while also serving satellites, space missions, and interplanetary exploration.
In this vision, the cloud becomes planetary—and eventually interplanetary.
Cooling, Power, and Performance: Space as the Ultimate Data Center
One of the most promising aspects of space-based AI is efficiency:
- Cooling: No water-based cooling or energy-hungry HVAC systems
- Power: Solar arrays provide clean, renewable energy
- Performance stability: No seismic activity, weather, or terrestrial interference
If scaled correctly, orbital AI data centers could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of AI training on Earth.
Environmental Impact: A Greener Path for AI?
AI’s carbon footprint is a growing concern. Large data centers consume enormous energy and water resources.
Space-based AI offers a potential alternative:
- Reduced reliance on Earth’s power grids
- Zero water consumption for cooling
- Lower heat pollution
- Long-term sustainability via solar energy
While launch costs and orbital debris remain challenges, Starcloud’s milestone suggests a greener future for AI infrastructure may lie above our atmosphere.
Security, Sovereignty, and Geopolitics of Space AI
Moving AI infrastructure into orbit raises new strategic questions:
- Who controls orbital AI platforms?
- How is data sovereignty enforced?
- Can space-based AI bypass regional restrictions?
- How are orbital AI assets protected?
Space-based AI could reshape global power dynamics, making AI infrastructure less tied to national borders—and potentially more contested.
Challenges Ahead: Space Is Not Easy
Despite the promise, significant hurdles remain:
- High launch and maintenance costs
- Radiation shielding requirements
- Limited physical repair options
- Space debris risks
- Regulatory uncertainty
Starcloud’s success is a proof of concept—not the final solution. Scaling orbital AI will require collaboration between governments, private industry, and space agencies.
The Future of Space Data Centers
Starcloud’s breakthrough may be the catalyst for:
- Fully autonomous orbital data centers
- AI-managed space infrastructure
- Real-time AI support for satellites and space missions
- Interplanetary AI networks
In the long term, space-based AI could become essential for deep-space exploration, asteroid mining, and off-world colonies.
Final Thoughts: The Dawn of Off-World Artificial Intelligence
Starcloud’s achievement marks the beginning of a new era—AI that is no longer confined to Earth. Training LLMs in space challenges our assumptions about computing, infrastructure, and the limits of technology.
As AI continues to grow in scale and ambition, the future may not lie in larger Earth-bound data centers—but in the silent, solar-powered expanses of orbit.
Artificial intelligence has crossed the planetary boundary. The age of off-world AI has begun.